In the WP or virtual stick function, when the aircraft suddenly hovers in flight or other abnormal phenomena, the cause is not confirmed and what troubleshooting needs to be done. The following provides relevant data cases to provide troubleshooting ideas.
1.
Phenomenon: Flight interruption.
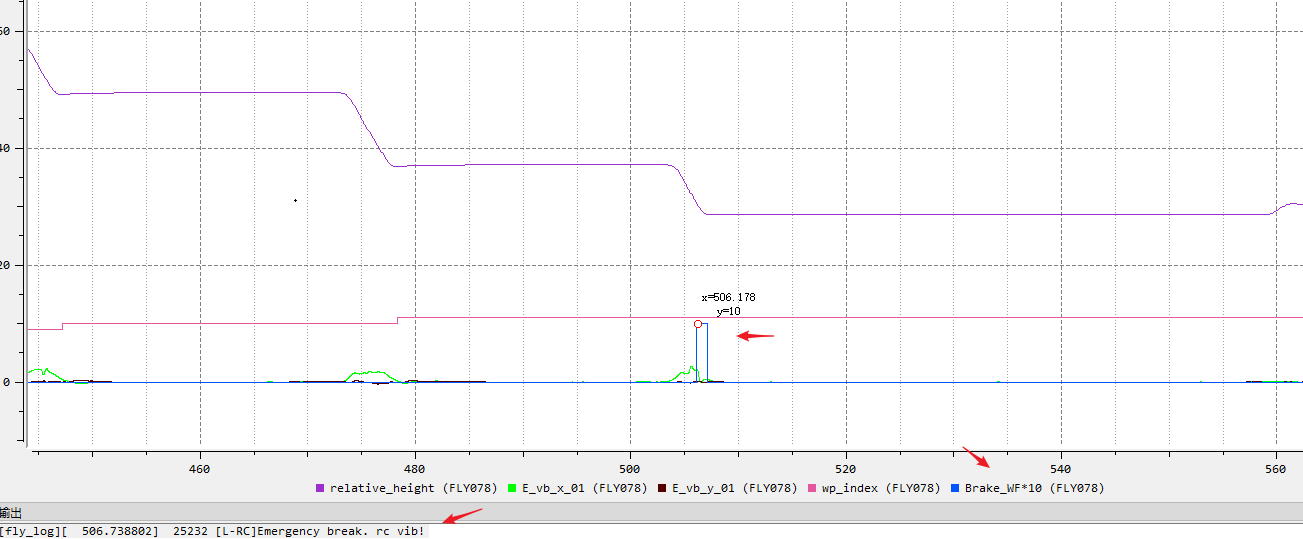
Cause: During WP flight, the aircraft detects obstacles that lead to WP mission interruption, as shown in the figure, obstacle avoidance is triggered when flying forward.
Troubleshooting idea: You can try to turn off obstacle avoidance for testing, but you should pay attention to the environment to ensure safe flight (note that the environment with too strong light may also trigger obstacle avoidance).
2,
Phenomenon: Flight interruption.
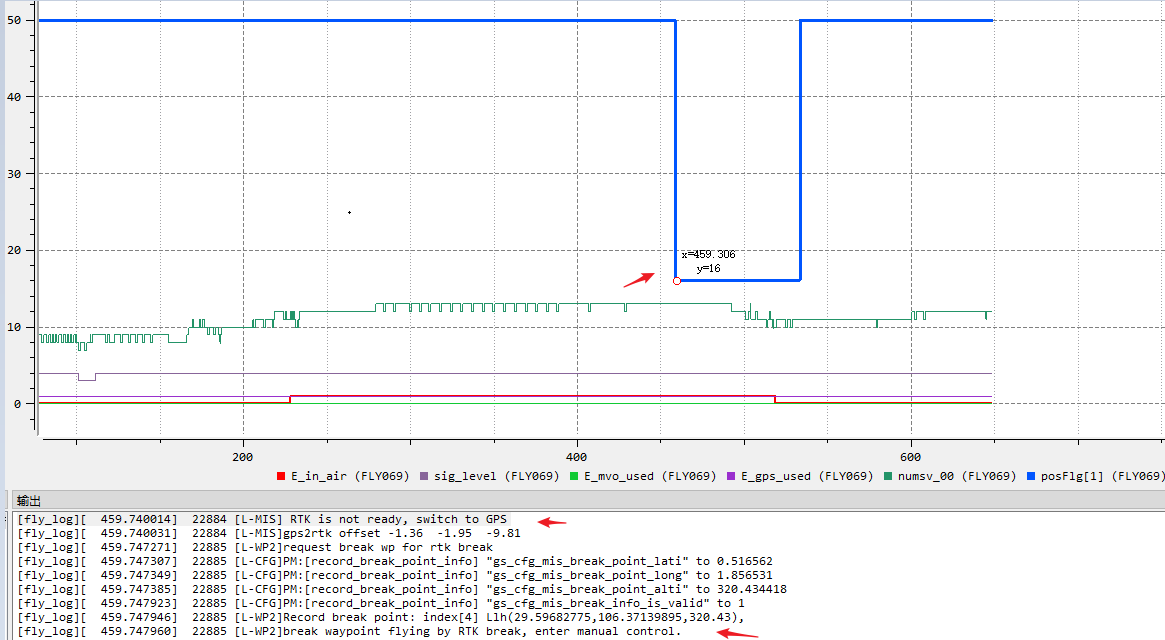
Cause: The status of RTK is abnormal, resulting in the termination of the WP mission. As shown in the figure, GPS signal is good, but the Positioning solution of RTK drops from 50 to 16.
Troubleshooting idea: Check the RTK status.
3,
Phenomenon: Flight interruption.
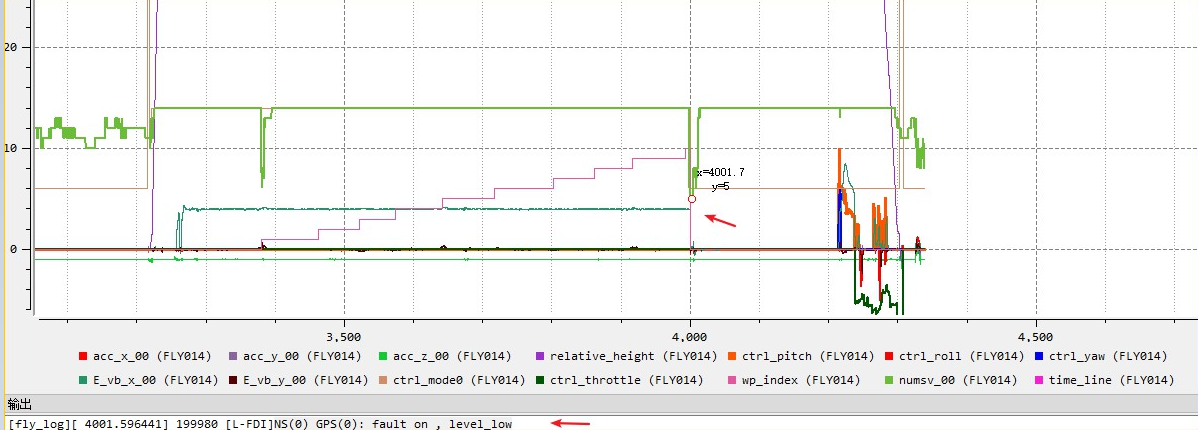
Cause: GPS signal suddenly weakened, resulting in flight interruption.
Troubleshooting idea: Check the GPS signal.
4,
Phenomenon: Flight interruption
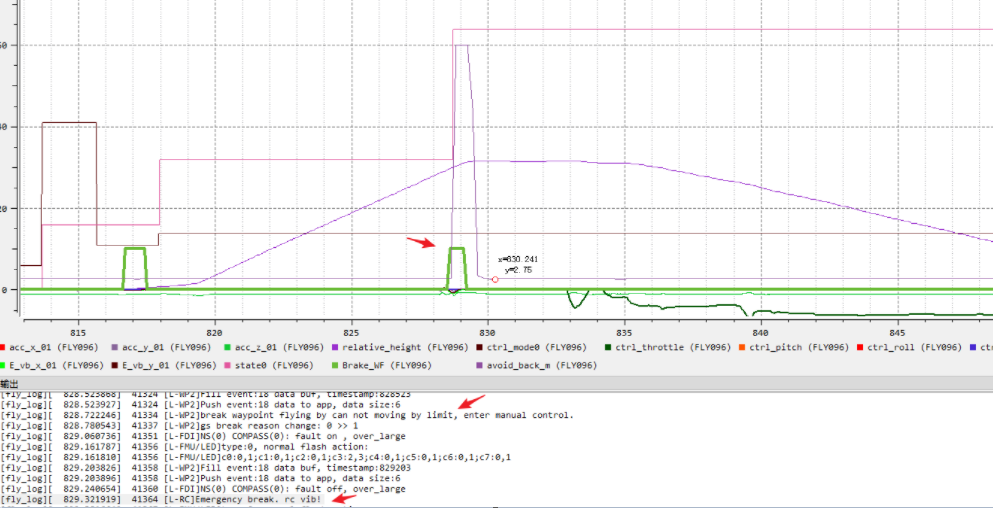
Cause: Aircraft sensors are suspected to be abnormal, and close objects are continuously detected. Obstacle avoidance is triggered in the WP to interrupt the WP mission.
Troubleshooting idea: You can use the official app to check whether the sensor in a certain direction continuously generates a close alarm in an open place. If you confirm this anomaly, it is suggested to send it for repair.
5,
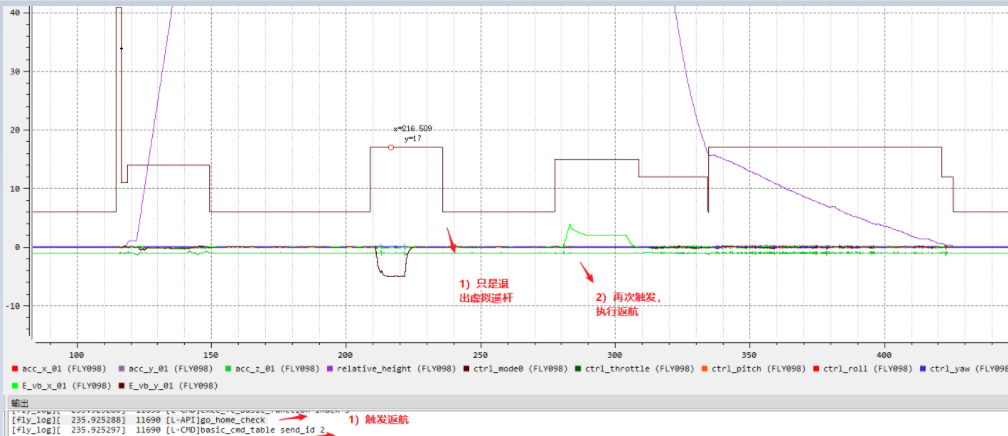
Phenomenon: The aircraft does not return home when OSDK is used in virtual joystick control to send return home command.
Cause: As shown in the figure below, the return command only causes the aircraft to exit the virtual stick function, send the return command again, and the aircraft starts to return home.
Troubleshooting idea: Need to exit the virtual stick first, and then send return home command.
6,
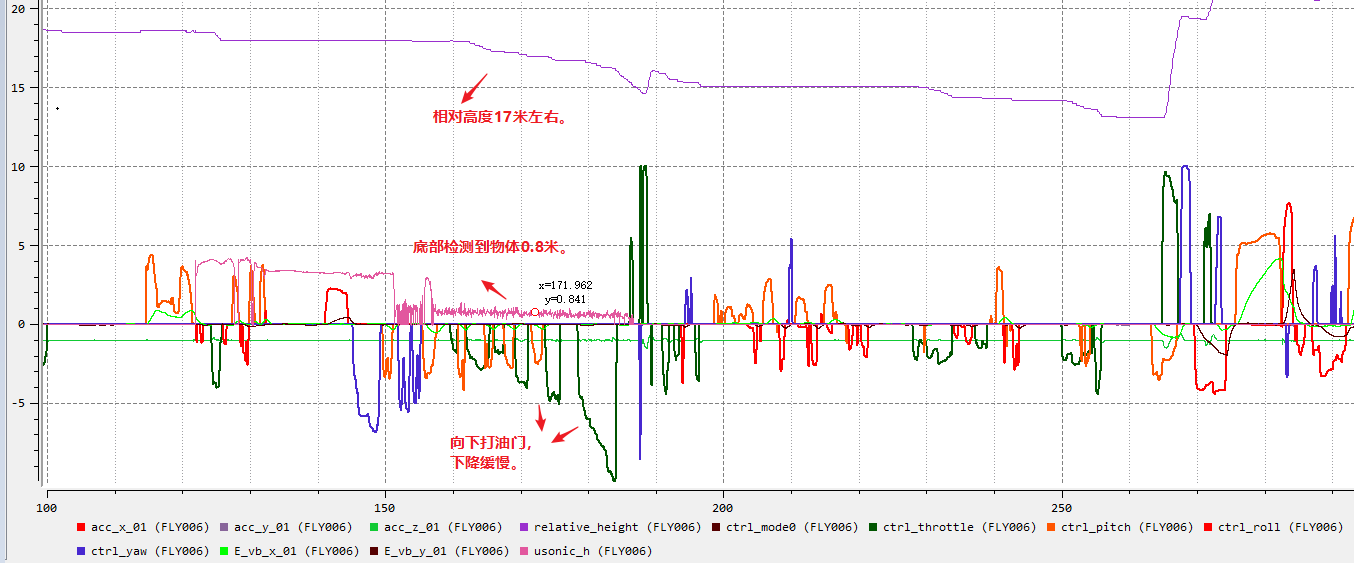
Phenomenon: Unable to descend at full speed, descent speed restricted.
Cause: The aircraft's sensors are suspected to be abnormal. Infrared sensors below continue to detect close objects, limiting the speed of descent.
Troubleshooting idea: You can use the official app to check whether the sensor below has a continuous close alarm when you are in an open place. If this abnormality is confirmed, it is suggested to send it for repair. Note that the sensor can also be affected in a foggy snow environment.
7,
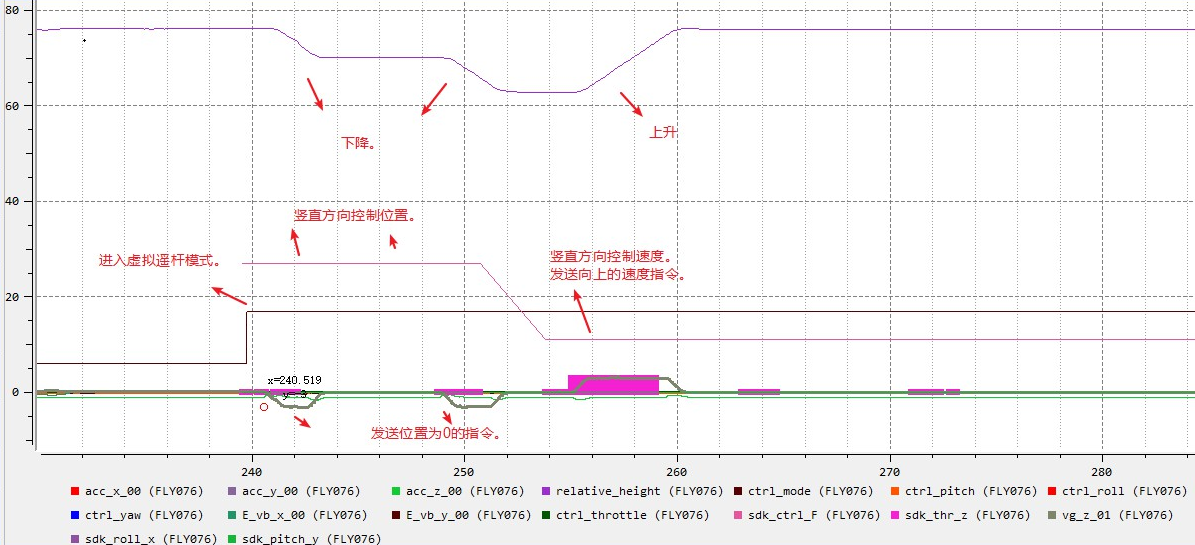
Phenomenon: the aircraft will descend when it sends a command in virtual stick mode. It is normal when it does not send a command.
Cause: The vertical direction control mode is position. When a command is sent, the command sent in the vertical direction is the position where the target point is 0, resulting in the aircraft descending.
Troubleshooting idea: Need to confirm the vertical direction control position or speed.
8,
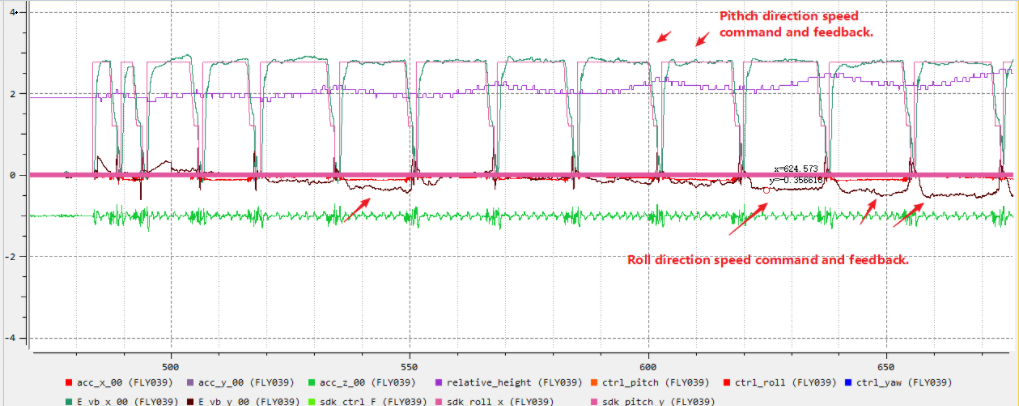
Phenomenon: The actual flight track of the aircraft does not match he WP mission.
Cause: The horizontal fusion speed of the aircraft is poor. For example, at a low altitude, the visual sensor participates in horizontal velocity detection, but the ground environment may be poor, resulting in inaccurate visual velocity. However, the fusion is involved, resulting in aircraft control errors.
Troubleshooting idea: Check the ground environment and GPS signal, and test to see if there is a problem after flying high in the open field (excluding visual).
9,
Phenomenon: Aircraft uncontrolled.
Cause: Compass is interfered by environment.
Troubleshooting idea: The problem is that the aircraft itself is affected by the environment, not the SDK. Flying with an official app may have the same problem. We need to calibrate the compass and try a different flight environment.
Conclusion:
If the above or other anomalies occur and further confirmation is needed, you can export flight control data by DJI Assistant 2 and submit it to technical support for further troubleshooting.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.